New features in Microsoft.Data.SqlClient 2.0 preview 3
Microsoft.Data.SqlClient is the .NET data provider for Microsoft SQL Server and Azure SQL Database. It is a union of the two legacy System.Data.SqlClient components which live independently in .NET Framework and .NET Core. Going forward, support for new SQL Server features will only be implemented in Microsoft.Data.SqlClient.
Version 2.0 of this driver is currently in preview, and in this blog post, I will take a closer look at some of the new features in the driver.
In order to try the preview, simply add a reference to the preview version in your project file:
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Data.SqlClient" Version="2.0.0-preview3.20122.2" />
EventSource traces
Adds support for capturing EventSource traces in .NET Framework, .NET Core, and .NET Standard applications. This allows you to capture traces from the "Microsoft.Data.SqlClient.EventSource" event source, using tools like PerfView and "dotnet trace" to capture events.
Create a .NET Core Console app to try it out:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<OutputType>Exe</OutputType>
<TargetFramework>netcoreapp3.1</TargetFramework>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Data.SqlClient" Version="2.0.0-preview3.20122.2" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
And add some code to Program.cs:
using (var sqlConnection = new SqlConnection("Data Source=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Initial Catalog=Northwind;Integrated Security= true"))
{
using (var sqlCommand = new SqlCommand("SELECT * FROM Shippers"))
{
sqlCommand.Connection = sqlConnection;
sqlConnection.Open();
var reader = sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
Remember to add this using: using Microsoft.Data.SqlClient;
We can now run this app from PerfView, and as you can see from the screenshot below, the collected information includes deep insights into for example the connection pool.
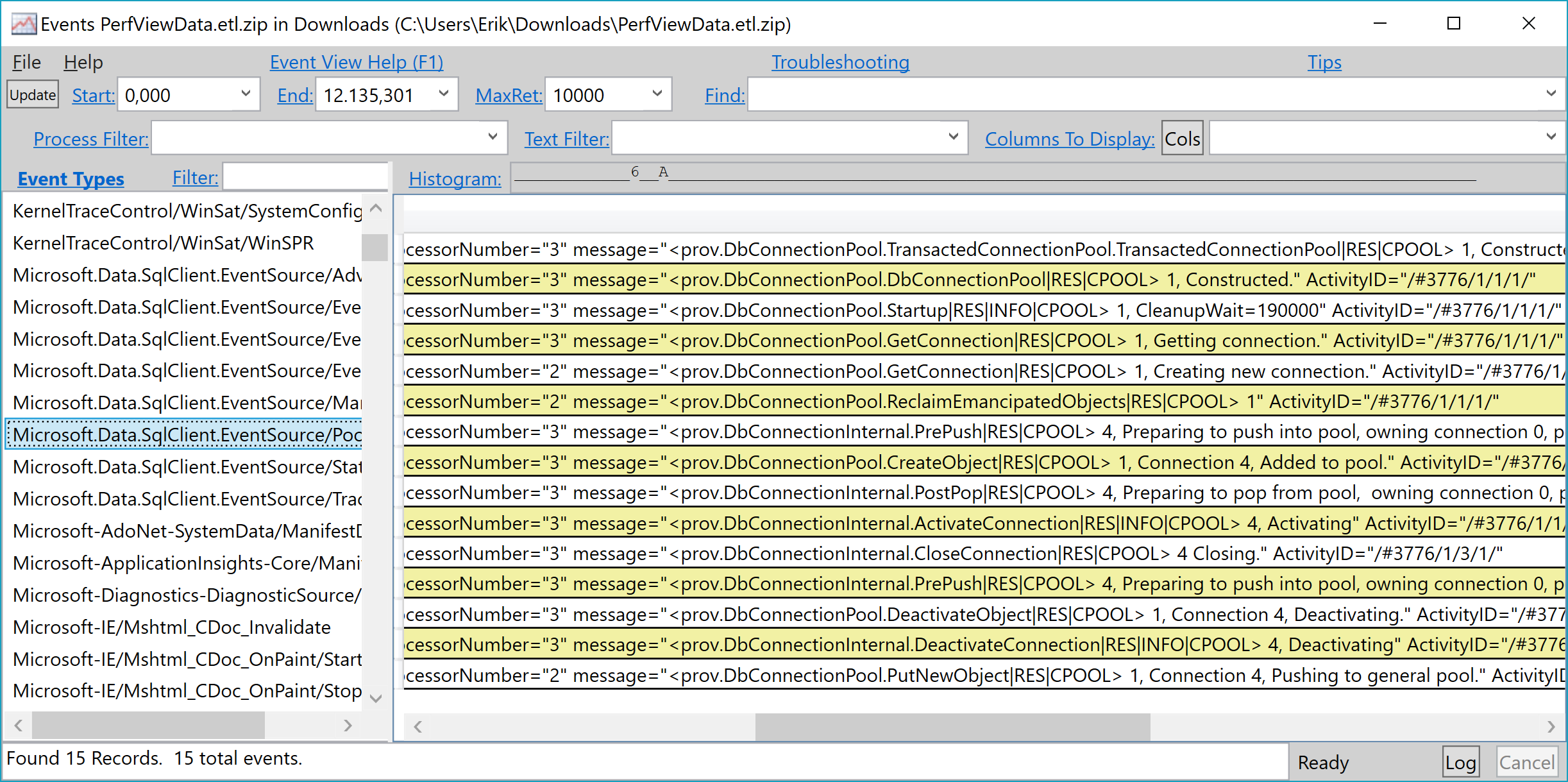
Managed networking layer enabled for Windows
Microsoft.Data.SqlClient contains two implementations of the layer that communicates with the network and translates network packages in the TDS protocol format.. By default, when using other platforms than Windows desktop, the implementation used is based on managed C# code, but when using Windows desktop, the networking layer is based on an unmanaged, closed source code (C/C++/assembly) implementation. Previously, when you were running .NET Core applications on Windows, you always used the unmanaged library (alledgely for performance reasons). But with version 2.0 preview 2, you can now opt-in to use the managed implementation.
Simply add the AppContext switch early in your application - before you use the SqlClient library. Keep in mind that this is currently for debug and development purposes only!
AppContext.SetSwitch("Switch.Microsoft.Data.SqlClient.UseManagedNetworkingOnWindows", true);
Running PerfView with the AppContext switch enabled, we can now see a new Event Type: Microsoft.Data.SqlClient.EventSource/SNITrace with events similar to this:
ThreadID="17.044" ProcessorNumber="2" message="<sc.SNI.LocalDB.Windows.LoadUserInstanceDll |SNI|INFO > User Instance DLL was loaded successfully." ActivityID="/#1688/1/1/1/2/"
ThreadID="17.044" ProcessorNumber="2" message="<sc.SNI.SNINpHandle.SNINpHandle |SNI|INFO> Constructor. server name = ., pipe name = localdb#b2ab8beb\tsql\query" ActivityID="/#1688/1/1/1/3/"
On a side note, as you can see from the performance measurements here, the fastest .NET SQL Server client is the one running .NET Core 3.1 and not .NET Framework. Another good reason to consider moving apps to .NET Core.
SqlBulkCopy - new RowsCopied property
After a SqlBulkCopy you may want to let the user the number of rows processed in the ongoing bulk copy operation for reporting and troubleshooting purposes. Previously, you either attach an event handler for the SqlRowsCopied event, or use reflection. Now, you can simply use the new RowsCopied property.
using (var sqlConnection = new SqlConnection("Data Source=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Initial Catalog=Northwind;Integrated Security= true"))
{
sqlConnection.Open();
using (var bulkCopy = new SqlBulkCopy(sqlConnection))
{
bulkCopy.DestinationTableName = "Shippers";
bulkCopy.WriteToServer(new DataTable());
var rows = bulkCopy.RowsCopied;
}
}
SqlConnection.Open() with fail fast option
You no longer need to change connection string to disable transient fault handling during the initial SqlConnection Open attempt.
In .NET 4.5.1, the System.Data.SqlClient was updated with two new connection string options: ConnectRetryCount and ConnectRetryInterval to support the idle connection resiliency feature available is SQL Server 2014 (and later) and Azure SQL DB.
The default value for connect retry count is 1, and the default value for connect retry interval is 10 seconds, meaning that in case a connection attempt fails, there will always be a 10 second delay until the first retry, unless the user explicitly specifies differently in the connection string. So using the default values for example to check if a user database exists by trying to connect to it will always cause a 10 second delay, something that EF Core does, and as described in the linked issue, connection string manipulation is not an option.
This problem has now been solved in preview 3, by addition of an OpenWithoutRetry option on the SqlConnection.Open method.
using (var sqlConnection = new SqlConnection("Data Source=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Initial Catalog=Northwind;Integrated Security= true"))
{
using (var sqlCommand = new SqlCommand("SELECT * FROM Shippers"))
{
sqlCommand.Connection = sqlConnection;
sqlConnection.Open(SqlConnectionOverrides.OpenWithoutRetry);
var reader = sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
Breaking changes
Since this preview is version 2, there are also a few breaking changes included.
SqlDataReader.GetSchemaTable()has been changed to return an emptyDataTableinstead of returning null when there are no columns.- Decimal parameters were truncated by SqlClient when precision and scale are set - see full explanation here
You can find the full release notes for the version 2 changes here.